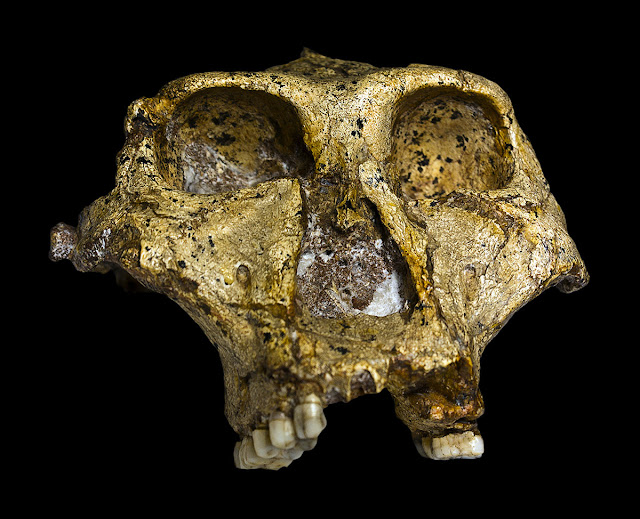
Africa plays a prominent business office inwards human evolution, in addition to is considered yesteryear researchers to live on the cradle of humanity. In the mid-20th century anthropologists flora fossils of Paranthropus robustus inwards South Africa, which belongs to an evolutionary side branch of Homo sapiens. Paranthropus robustus lived merely about 2 i K one thousand years agone but eventually died out. Possible reasons for the extinction own got straightaway been brought to low-cal yesteryear an international squad of anthropologists in addition to geoscientists led yesteryear medico Thibaut Caley of the University of Bordeaux. In this effort, the researchers, who include medico Lydie Dupont in addition to medico Enno Schefuß of MARUM – Center for Marine Environmental Sciences at the University of Bremen combined diverse indicators to reconstruct the climatic weather inwards southeast Africa at this time. The results were straightaway published inwards the mag Nature.
Due to the continuous deposition, marine sediment cores let the researchers to notice a sequence of climate changes over long periods of time. Microfossils in addition to pollen from the province are every bit good washed into the sea yesteryear the Limpopo in addition to deposited on the sea floor. This allows the findings from sites on province to live on compared to their temporal development. As medico Lydie Dupont from MARUM notes, information from the province oftentimes solely comprehend brusque fourth dimension periods, but they tin sack furnish of import clues almost the occurrences of species in addition to their nutrient sources. With the handle of the sediment cores, the scientists had access to a climate tape spanning almost 2.14 i K one thousand years.
The squad combined real dissimilar kinds of analyses. Hydrogen every bit good every bit carbon isotopes of molecular flora fossils were investigated, in addition to these were compared amongst the results of pollen analyses in addition to chemical cistron compositions. Each analysis lone tin sack live on interpreted inwards dissimilar ways. "Only through the comprehensive consideration could a coherent pic of the climate inwards the Limpopo percentage live on reconstructed," says Lydie Dupont.
Furthermore, the squad determined the changes inwards sea-surface temperatures for this fourth dimension period, allowing them to assess the influence of the sea on the climate on land. Combining their results amongst information from the literature, the researchers were able to depict conclusions almost the causes of climate changes that occurred during the fourth dimension when Paranthropus robustus lived in addition to ultimately died out.
The combined results from Limpopo portray a dissimilar pic than the report from Lake Malawi. From almost 1 i K one thousand years agone to 600,000 years agone climate became substantially to a greater extent than arid. At the same time, climate variability increased noticeably. "What eventually led to the extinction is hard to say," says medico Enno Schefuß. Climatic changes e'er Pb to adaptations yesteryear organisms – including adaptation of their feeding habits. If the weather alter extremely speedily over a brusque menses of time, organisms are less apt to adjust evolutionarily to the altered circumstances. According to the findings inwards the Limpopo region, Paranthropus robustus died out 600,000 years ago.
Source: University of Bremen [July 10, 2018]
Sumber http://archaeologynewsnetwork.blogspot.com
Buat lebih berguna, kongsi: