Long-term observations of surface temperatures present an intensified surface warming inwards Canada, Siberia, Alaska in addition to inwards the Arctic Ocean relative to global hateful temperature rise. This warming pattern, ordinarily referred to equally Arctic amplification, is consistent alongside figurer models, simulating the response to increasing greenhouse gas concentrations. However, the underlying physical processes for the intensified warming notwithstanding stay elusive.
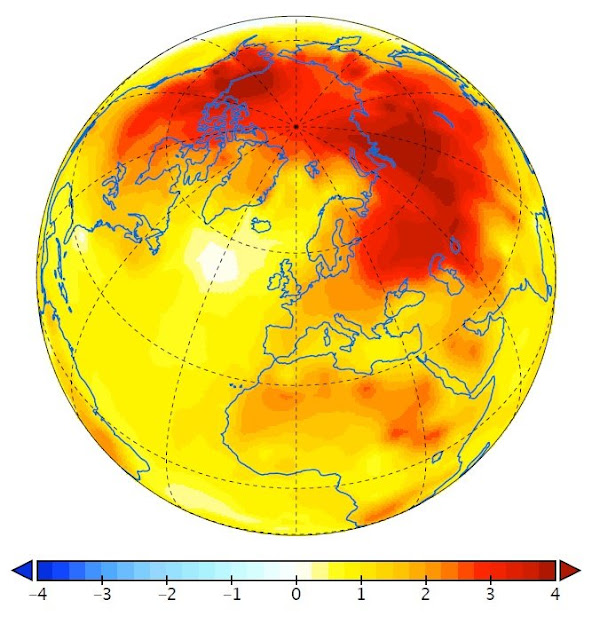 |
| The observations present a clear enhancement of warming In the Arctic part in addition to across Siberia, Northern Canada in addition to Alaska [Credit: Institute for Basic Science (IBS)] |
"Our report clearly shows that local carbon dioxide forcing in addition to polar feedbacks are nigh effective inwards Arctic amplification compared to other processes", said corresponding writer Malte Stuecker, projection leader at the IBS Center for Climate Physics (ICCP) inwards Busan, South Korea.
Increasing anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations trap oestrus inwards the atmosphere, which leads to surface warming. Regional processes tin in addition to then farther amplify or dampen this effect, thereby creating the typical pattern of global warming. In the Arctic region, surface warming reduces snowfall in addition to sea-ice extent, which inwards plough decreases the reflectivity of the surface. As a result, to a greater extent than sunlight tin accomplish the plough over of layers of the soil in addition to ocean, leading to accelerated warming. Furthermore, changes inwards Arctic clouds in addition to of the vertical atmospheric temperature profile tin heighten warming inwards the polar regions.
In add-on to these factors, oestrus tin hold upward transported into the Arctic past times winds. "We come across this procedure for illustration during El Niño events. Tropical warming, caused either past times El Niño or anthropogenic greenhouse emissions, tin displace global shifts inwards atmospheric conditions patterns, which may atomic number 82 to changes inwards surface temperatures inwards remote regions, such equally the Arctic", said Kyle Armour, co-author of the report in addition to professor of Atmospheric Sciences in addition to Oceanography at the University of Washington.
Moreover, global warming exterior the Arctic part volition equally good atomic number 82 to an increase inwards Atlantic Ocean temperatures. Ocean currents, such equally the Gulf Stream in addition to the North Atlantic drift tin in addition to then carry the warmer waters to the Arctic ocean, where they could melt sea H2O ice in addition to sense farther amplification due to local processes.
To decide whether tropical warming, atmospheric current of air in addition to sea electrical flow changes contribute to hereafter Arctic Amplification, the squad designed a serial of figurer model simulations. "By comparison simulations alongside entirely Arctic CO2 changes alongside simulations that apply CO2 globally, nosotros observe like Arctic warming patterns. These findings demonstrate that remote physical processes from exterior the polar regions create non play a major role, inwards contrast to previous suggestions", says co-author Cecilia Bitz, professor of Atmospheric Sciences at the University of Washington.
In the torrid zone - fueled past times heat in addition to wet - air tin easily displace upward to high altitudes, pregnant the atmosphere is unstable. In contrast, the Arctic atmosphere is much to a greater extent than stable alongside observe to vertical air movement. This status enhances the CO2-induced warming inwards the Arctic nigh the surface. In the torrid zone - due to the unstable atmosphere - CO2 to a greater extent than oft than non warms the upper atmosphere in addition to unloose energy is easily lost to space. This is contrary to what happens inwards the Arctic: Less outgoing infrared radiations escapes the atmosphere, which farther amplifies the surface-trapped warming.
"Our figurer simulations present that these changes inwards the vertical atmospheric temperature profile inwards the Arctic part outweigh other regional feedback factors, such equally the often-cited ice-albedo feedback" says Malte Stuecker.
The novel findings of this report highlight the importance of Arctic processes inwards controlling the footstep at which sea-ice volition retreat inwards the Arctic Ocean. The results are equally good of import to empathize how sensitive polar ecosystems, Arctic permafrost in addition to the Greenland ice-sheet volition response to Global Warming.
Source: Institute for Basic Science [November 19, 2018]
Sumber http://archaeologynewsnetwork.blogspot.com
Buat lebih berguna, kongsi:
