An odd infrared calorie-free emission from a nearby neutron star detected past times NASA's Hubble Space Telescope could holler for novel features never earlier seen. One possibility is that in that place is a dusty disk surrounding the neutron star; some other is that in that place is an energetic current of air coming off the object as well as slamming into gas inwards interstellar infinite the neutron star is plowing through.
 |
This example shows a neutron star (RX J0806.4-4123) amongst a disk of warm dust that produces an infrared signature
as detected past times NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The disk wasn't straight photographed, but i agency to explicate the data
is past times hypothesizing a disk construction that could endure xviii billion miles across. The disk would endure made upward of material
falling dorsum onto the neutron star afterwards the supernova explosion that created the stellar remnant
[Credit: NASA, ESA, as well as N. Tr'Ehnl (Pennsylvania State University)] |
Although neutron stars are mostly studied inwards radio as well as high-energy emissions, such equally X-rays, this report demonstrates that novel as well as interesting information nearly neutron stars tin post away too endure gained past times studying them inwards infrared light, tell researchers.
The observation, past times a squad of researchers at Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania; Sabanci University, Istanbul, Turkey; as well as the University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, could assist astronomers improve sympathise the development of neutron stars -- the incredibly dense remnants afterwards a massive star explodes equally a supernova. Neutron stars are too called pulsars because their real fast rotation (typically fractions of a second, inwards this instance eleven seconds) causes time-variable emission from light-emitting regions.
"This detail neutron star belongs to a grouping of vii nearby X-ray pulsars -- nicknamed 'the Magnificent Seven' -- that are hotter than they ought to endure considering their ages as well as available liberate energy reservoir provided past times the loss of rotation energy," said Bettina Posselt, associate query professor of astronomy as well as astrophysics at Pennsylvania State as well as the Pb writer of the paper. "We observed an extended surface area of infrared emissions about this neutron star -- named RX J0806.4-4123 -- the total size of which translates into nearly 200 astronomical units (approximately xviii billion miles) at the assumed distance of the pulsar."
 |
This is a neutron star amongst a pulsar current of air nebula produced past times the interaction of the pulsar current of air as well as the oncoming
interstellar medium. H5N1 pulsar current of air nebula could explicate the extended infrared emission observed past times astronomers
around the neutron star RX J0806.4-4123. Such an infrared-only pulsar current of air nebula is odd because
it implies a rather depression liberate energy of the accelerated particles [Credit: Nahks Tr'Ehnl, Penn State] |
This is the starting fourth dimension neutron star inwards which an extended signal has been seen solely inwards infrared light. The researchers propose ii possibilities that could explicate the extended infrared signal seen past times Hubble. The starting fourth dimension is that in that place is a disk of cloth -- perchance mostly dust -- surrounding the pulsar.
"One theory is that in that place could endure what is known equally a 'fallback disk' of cloth that coalesced about the neutron star afterwards the supernova," said Posselt. "Such a disk would endure composed of affair from the progenitor massive star. Its subsequent interaction amongst the neutron star could convey heated the pulsar as well as slowed its rotation. If confirmed equally a supernova fallback disk, this trial could alter our full general agreement of neutron star evolution."
The minute possible explanation for the extended infrared emission from this neutron star is a "pulsar current of air nebula."
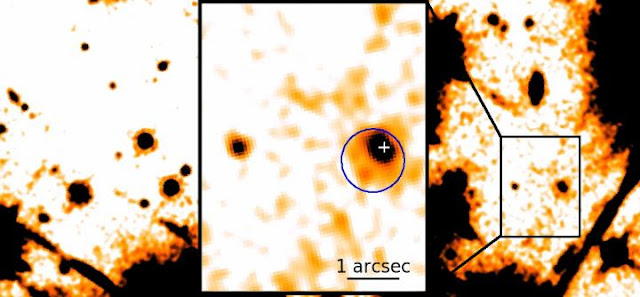 |
This is an infrared icon of a neutron star (source on correct inwards box) amongst an extended infrared emission obtained from
observations amongst the Hubble Space Telescope. The bluish circle indicates the pulsar's X-ray pose (obtained
with the Chandra X-ray Space Telescope), the cross marks the pose of the pulsar inwards the UV-Optical
(measured amongst the Hubble Space Telescope) [Credit: Bettina Posselt, Penn State] |
"A pulsar current of air nebula would necessitate that the neutron star exhibits a pulsar wind," said Posselt. "A pulsar current of air tin post away endure produced when particles are accelerated inwards the electrical plain that is produced past times the fast rotation of a neutron star amongst a potent magnetic field. As the neutron star travels through the interstellar medium at greater than the speed of sound, a stupor tin post away cast where the interstellar medium as well as the pulsar current of air interact. The shocked particles would as well as then emit synchrotron radiation, causing the extended infrared signal that nosotros see. Typically, pulsar current of air nebulae are seen inwards X-rays as well as an infrared-only pulsar current of air nebula would endure real odd as well as exciting."
Using NASA's upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers volition endure able to farther explore this newly opened regain infinite inwards the infrared to improve sympathise neutron star evolution.
H5N1 newspaper describing the query as well as ii possible explanations for the odd finding appears inwards the
Astrophysical Journal.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center [September 17, 2018] Sumber http://archaeologynewsnetwork.blogspot.com



