Phytoplankton blooms that shape the base of operations of the marine nutrient spider web are expanding northward into ice-free waters where they convey never been seen before, according to novel research.
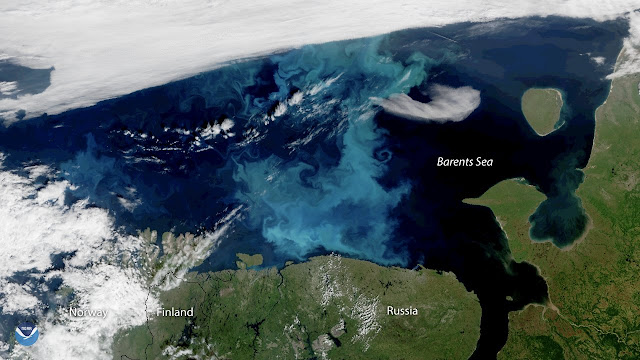 |
| This true-colour image, captured yesteryear the NOAA-20 satellite on July 30, 2018, shows a large phytoplankton bloom in the Barents Sea [Credit: NOAA Environmental Visualization Laboratory] |
The turn down inward Arctic sea H2O ice over the yesteryear several decades has made way for areas of opened upward H2O where phytoplankton tin thrive, driving their northward expansion, according to the study's authors. The researchers are unsure what effect this expansion volition convey on the nutrient web, only the results advise the turn down of H2O ice covert is impacting marine ecosystems inward unforeseen ways.
If sea H2O ice continues to decline, it could drive phytoplankton saltation blooms further northward too increment primary productivity fifty-fifty more. These changes could touching on the fate of the Arctic Ocean equally a carbon source or a carbon sink, according to the study.
"If the H2O ice pack totally disappears inward summer, at that spot volition move consequences for the phytoplankton saltation bloom," said Sophie Renaut, a Ph.D. educatee at Laval University inward Quebec City, Canada, too Pb writer of the novel written report inward Geophysical Research Letters, a periodical of the American Geophysical Union. "We cannot just predict how it volition evolve, only we're pretty certain at that spot are going to move drastic consequences for the entire ecosystem."
Phytoplankton inward the ecosystem
Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that alive inward water, eat carbon dioxide too discover oxygen through photosynthesis. In this process, they convert sunlight into chemic energy. Phytoplankton shape the base of operations of the marine nutrient web, indirectly feeding everything from pocket-sized fish to multi-ton whales.
Phytoplankton growth depends on the availability of carbon dioxide, sunlight, nutrients, H2O temperature too salinity, H2O depth too grazing animals, according to the NASA basis Observatory. When weather are ideal, phytoplankton population growth tin explode, or bloom. While a blossom may terminal several weeks, the lifespan of an private phytoplankton is seldom to a greater extent than than a few days.
Phytoplankton inward the Arctic Ocean typically blossom every spring. In the past, phytoplankton blooms convey been virtually absent from the highest Arctic latitudes, because these areas are normally covered yesteryear sea ice. In recent decades sea H2O ice has declined, breaking upward before inward the saltation or non forming at all inward or too so areas of the Arctic.
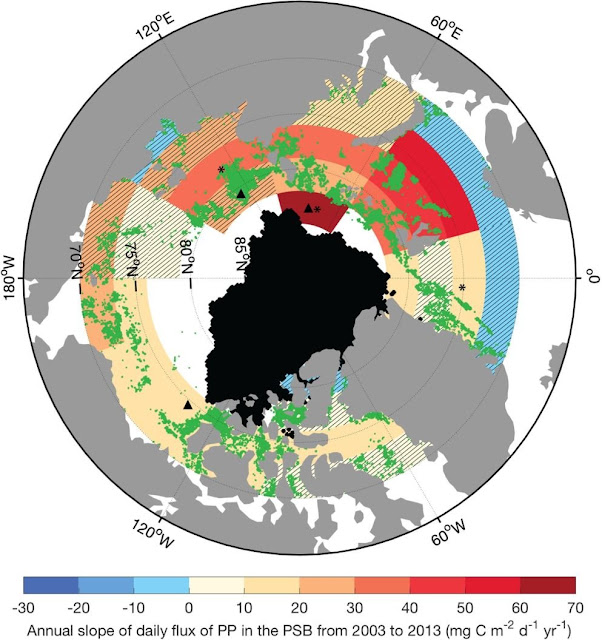
They constitute the saltation blooms are expanding further northward too increasing inward primary productivity. In the saltation too summertime months, cyberspace primary productivity inward the Arctic Ocean increased yesteryear 31 per centum betwixt 2003 too 2013, according to the study. The researchers too constitute that these blooms inward the Barents too Kara Seas, northward of Russia, are expanding northward at a charge per unit of measurement of 1 flat of latitude per decade.
Unexpected effects of sea H2O ice decline
Sea H2O ice melt occurring before inward the flavor creates larger opened upward H2O areas that deed equally incubators for phytoplankton growth too elongate their growing season, according to Renaut.
The authors suspect saltation blooms could someday extend into the Arctic's fundamental basin, which encompasses most everything northward of fourscore degrees latitude. Primary productivity, though, would probable remain depression due to a lack of nutrients. Less H2O ice covert agency saltation blooms too under-ice blooms may too convey to compete for calorie-free too nutrients, so altering the menses of the marine ecosystem. The results advise a large alter inward this region, which has never been gratuitous of H2O ice cover.
"The polar regions--the Antarctic Ocean too the Arctic Ocean--they're actually of import because they play a critical business office inward regulating the global climate," Renaut said. "If sea H2O ice disappears completely inward summertime inward the Arctic Ocean, which is what nosotros aspect inward or too so decades, it's going to convey an impact on the ecosystem only too probable on the climate."
Patricia Yager, professor of Marine Sciences at the University of Georgia who was non involved amongst the novel study, said the before algal blossom growth they observed inward or too so areas could convey considerable impacts if animals are non even too so gear upward to graze on the phytoplankton.
"Such a mismatch inward fourth dimension could campaign major changes to the Arctic nutrient web, impacting non solely the local animals too the people who alive there, only too the global population of migrating animals who depend on these Arctic resources," Yager said. "What happens inward the Arctic does non remain inward the Arctic."
Cecile Rousseaux, a interrogation scientist at the Universities Space Research Association, who was non involved inward the novel study, said the written report advances interrogation inward this expanse yesteryear investigating private regions of the Arctic for phytoplankton productivity, too represents prove of the effects that reduced H2O ice covert convey on the biochemical cycle of the Arctic Ocean. However, Rousseaux noted that the written report does convey limitations.
"It is too of import to recall that nosotros are currently express yesteryear the amount of information available to written report these changes," Rousseaux said. "Longer fourth dimension serial of satellite information volition allow us to confirm whether these trends inward phytoplankton productivity persist or not."
Source: American Geophysical Union [October 16, 2018]
Sumber http://archaeologynewsnetwork.blogspot.com
Buat lebih berguna, kongsi: