Accurate projections of body of body of water score rising require sophisticated models for glacier flow, but electrical current approaches create a pitiable task capturing the physical processes that command how fast glaciers slide over sediments, according to University of Oregon researchers.
 |
| UO postdoctoral researcher Colin Meyer reaches alongside an H2O ice axe on frozen sediment beneath a glacier inwards Alaska [Credit: Kiya Riverman] |
Detailed inwards a July article inwards the periodical Nature Communications, the approach captures how the amount of sediment frozen to a glacier's base of operations varies alongside the underlying H2O pressure, melting charge per unit of measurement in addition to particle size. It helps concern human relationship for resulting changes inwards frictional resistance to glacier sliding.
To illustrate their theory, the UO researchers noted that regardless of the size or weight of a glacier, sliding accommodates H2O ice menstruum that is driven past times gravity in addition to adjusts surface slopes in addition to then that friction at the bed never exceeds to a greater extent than than close 1 bar of stress.
"This is a longstanding problem," Meyer said. "If nosotros desire to forecast what glaciers are going to create inwards the future, nosotros induce got to utter close the identify that nosotros can't see: the interface betwixt the H2O ice in addition to the bed."
Formulations dating from the early on 1950s attributed this upper stress bound to the plastic-like nature of H2O ice deformation. In their paper, however, the UO researchers noted that fifty pct of all glaciers, including those that displace the most H2O ice off province inwards Greenland in addition to Antarctica into the sea, are sliding.
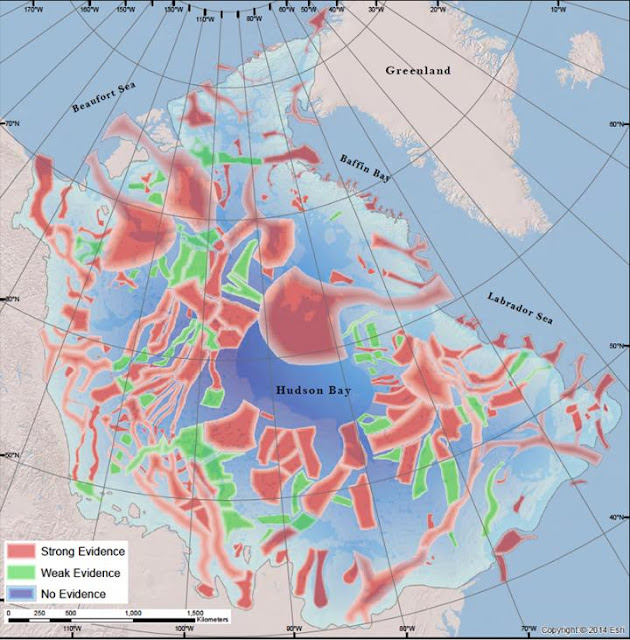 |
| Map shows areas inwards North America’s Laurentide Ice Sheet where in that location is rigid evidence for glacial sliding [Credit: University of Oregon] |
"Nye's function carried the caveat that the formula entirely industrial plant for non-sliding areas," said Alan Rempel, a professor inwards the UO's Department of globe Sciences in addition to the paper's senior author. "It's non the consummate story. It entirely applies if the glacier is stuck."
Using their novel theory, which combined mathematical analysis alongside satellite information in addition to geological testify from regions previously covered past times H2O ice sheets, the UO squad matched the 1 bar limit. The number provided confidence that freezing sediments is the physical procedure that controls the friction of the ice-sediment interface. The importance of freezing sediment, Meyer said, volition live influential inwards developing to a greater extent than accurate H2O ice menstruum models.
The theory's incorporation of freezing sediment provides a to a greater extent than consummate sentiment of glacial movement, Rempel said. "It focuses on the sliding in addition to should assist scientists accurately discovery the velocity of an advancing or receding glacier."
"If nosotros desire to empathise how fast body of body of water levels are going to rise, nosotros demand to know how fast the H2O ice sheets are going to disintegrate," Meyer said. "We demand to empathise the usage of friction at the base of operations of a big glacier. Does H2O lubricate the interface or is the glacier frozen to the sediments? This friction sets how fast glaciers tin flow."
The charge per unit of measurement of sliding, Rempel said, is fundamental to agreement impacts on body of body of water level.
"The hypothesis that we've pushed forrard is that the physics of how glacier H2O ice interacts alongside its bed is precisely the same physics equally how H2O ice interacts alongside dirt inwards the public around us," Rempel said. "What we've looked at are weather nether which H2O ice volition simply slide over dirt versus when H2O ice sinks into in addition to takes the dirt along alongside it."
Incorporating frozen sediment into sliding laws, Rempel said, volition Pb to to a greater extent than accurate projections of body of body of water score rising based on glacier-related conditions.
Author: Jim Barlow | Source: University of Oregon [September 03, 2018]
Sumber http://archaeologynewsnetwork.blogspot.com
Buat lebih berguna, kongsi:
